
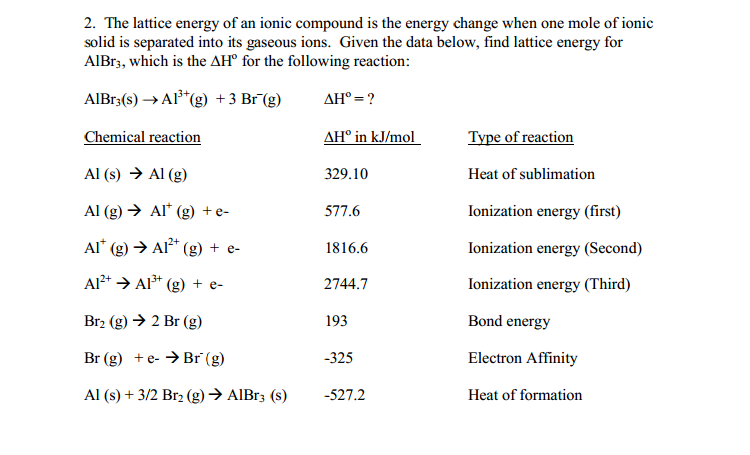
The enthalpy change in this step is the negative of the lattice energy, so it is also an exothermic quantity. These ions combine to produce solid cesium fluoride. Now, one mole of Cs cations and one mole of F anions is present.Converting one mole of fluorine atoms into fluoride ions is an exothermic process, so this step gives off energy (the electron affinity).In the next step, the energy required to break the F–F bond to produce fluorine atoms needs to be accounted for.The Δ H s° represents the conversion of solid cesium into a gas (sublimation), and then the ionization energy converts the gaseous cesium atoms into cations.Consider the elements in their most common states, Cs ( s) and F 2 ( g).Negative of the lattice energy of CsF ( s)Įnthalpy of formation of CsF ( s), add steps 1–5
#Lattice energy equation ke series#
The Born-Haber cycle is an application of Hess’s law that breaks down the formation of an ionic solid into a series of individual steps: Enthalpy of sublimation of Cs ( s) However, the lattice energy can be calculated using a thermochemical cycle. It is not possible to measure lattice energies directly.
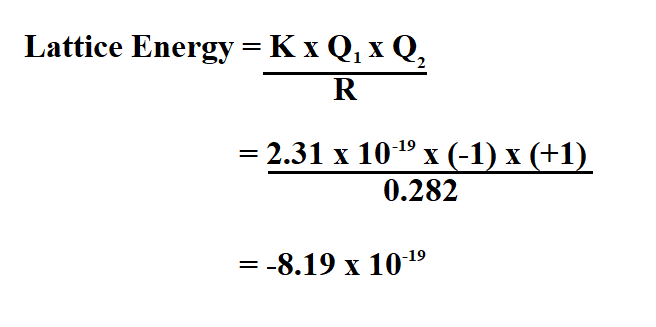
Determination of Lattice Energy of an Ionic Compound When one mole each of gaseous Na + and Cl – ions form solid NaCl, 769 kJ of heat is released. Thus, it requires 769 kJ to separate one mole of solid NaCl into gaseous Na + and Cl – ions. For sodium chloride, Δ H lattice = 769 kJ. In both cases, a larger magnitude for lattice energy indicates a more stable ionic compound. Thus, make sure to confirm which definition is used when looking up lattice energies in another reference. Another way is to use an equivalent, but opposite convention, wherein the lattice energy is exothermic (negative values) and described as the energy released when ions combine to form a lattice. Here, the convention is used where the ionic solid is separated into ions, meaning the lattice energies will be endothermic (positive values). The lattice energy (Δ H lattice) of an ionic compound is defined as the energy required to separate one mole of the solid into its component gaseous ions. The lattice energy of a compound is a measure of the strength of this attraction. Meaning the enthalpy value of the direct route equals the sum of enthalpies of the five steps.īy solving the equation for lattice energy, a large negative value is determined, which signifies an exothermic reaction.Īn ionic compound is stable because of the electrostatic attraction between its positive and negative ions. Hess’s law states that the change in the overall enthalpy of a stepwise process is the sum of the enthalpy changes of each step. In the final step, the electrostatic attraction between the gaseous ions leads to the formation of the lattice structure. The electron is then taken up by the gaseous chlorine to form a chloride anion. An electron is removed from the gaseous sodium to form a sodium cation. The third and fourth steps account for the electron transfer to form ions. Next, diatomic chlorine molecules dissociate into gaseous chlorine atoms. In the first step, solid-state sodium is converted into its gaseous form. The direct route represents the standard enthalpy of formation of NaCl from elemental sodium and chlorine. However, it can be calculated using Hess’s law in a hypothetical series of steps called the Born–Haber cycle, which represents the formation of an ionic compound from its constituent elements.įor example, the Born-Haber cycle for sodium chloride formation considers two alternate routes, one direct and another indirect. In a solid ionic compound, a large number of charged particles interact with each other making it difficult to determine the exact value of the lattice energy experimentally. The total energy associated with the formation or breakdown of a crystalline lattice into its gaseous constituents is called lattice energy.

The resulting lattice structure is stabilized by decreasing the potential energy, which is released as heat, an exothermic reaction. But where is the energy coming from?Īccording to Coulomb’s law, cations and anions are attracted to each other by strong electrostatic forces into a solid array or lattice. However, when elemental sodium and chlorine react to form a solid sodium chloride crystal, it's a highly exothermic process. Formation of ionic bonds requires an electron transfer from a metal to a nonmetal atom - a process that is often endothermic.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
